Boiling three Xiang four water, gather refrigeration elite! Fu Jing welding wonderful appearance 2021 China refrigeration industry innovation achievements transformation forum!
Release time:
2021-07-29
【Summary Description】 Fujing Welding was invited to participate in the 2021 China Refrigeration Industry Innovation and Upgrading Achievement Transformation Forum. With its excellent innovation strength, it won the Innovation Achievement Transformation Award, and its brand strength was highly recognized.
Transformation of integration and innovation achievements

Industrial innovation and upgrading lead the development of the industry
From September 10 to 12, the 2021 (6th) China International Food and Catering Expo, sponsored by the Ministry of Commerce and the people's Government of Hunan Province, was held in Changsha International Convention and Exhibition Center. Compared with previous editions, this year's Food Expo has added an exhibition area for refrigeration equipment,At the same time, the 2021 China Refrigeration Industry Innovation and Upgrading Achievement Transformation Forum was held, and Fujing Welding was invited to participate in the exhibition.We will jointly explore the new pattern of refrigeration ecology, display innovative welding products and one-stop solutions, and participate in the industry event with refrigeration colleagues.

Experts and scholars gather to welcome the new bureau of refrigeration industry
On the afternoon of September 10, the "2021 China Refrigeration Industry Innovation Achievement Transformation (Changsha) Forum" officially kicked off in Hall E4 of Changsha International Convention and Exhibition Center, which attracted enthusiastic attention among food, catering, and refrigeration people.
At the forum, Mr. Ying Feng, deputy general manager of Fujing Welding Technology Co., Ltd, was Hangzhou to share Fujing's efficient, environmentally friendly and clean welding products from various angles, providing assistance for improving the quality of the refrigeration industry chain and solving welding problems.

Site Sharing: How to Solve the Welding Problem of Refrigeration Headache?
In the entire refrigeration equipment installation and operation, many people ignore the Welding materials selection and operation, resulting in the presence of impurities in the weld or pores and trachoma, affecting the normal operation of the unit.
Through the control of composition, impurities, gas content and organization, Fujing welding can make the product cleaner and more stable, thus solving the problems of unstable welding, trachoma and pores after welding.
Taking Fujing No. 0 welding rod as an example, by digging deep into the operation difficulties and investigating the customer's pain points, the research and development team improved the overall performance of the phosphorus copper welding rod on the basis of the standard phosphorus copper welding rod to meet the customer's demand for high-performance welding rod.
In order to respond to the requirements of green environmental protection and energy saving and emission reduction, a variety of composite brazing materials have been introduced, which have been widely used in refrigeration and auto parts industries to effectively control the amount of flux used and reduce the process of applying flux.

Under the guidance of the national carbon peak and carbon neutral index, Fujing is constantly providing customers with welding solutions instead of flame brazing and manual brazing to improve efficiency and reduce carbon emissions.
This time Fujing welding brought Fujing No. 0, phosphor copper electrode, Fujing DG electrode, aluminum flux core series and other self-developed products to the conference, attracting a large number of visitors to stop and watch.
Fujing welding adopts cleaner solder alloy, which has higher wetting and caulking performance, breaking the monopoly of foreign high-performance electrodes in the market for a long time.
It is of great significance to the technological progress of the entire Welding materials, so that friends in the refrigeration industry can no longer spend high costs and can use high-performance phosphor bronze electrodes.
At the award ceremony of this forum, Fujing Welding won the Innovation Achievement Transfer Award for its excellent innovation strength, and its brand strength was highly recognized.
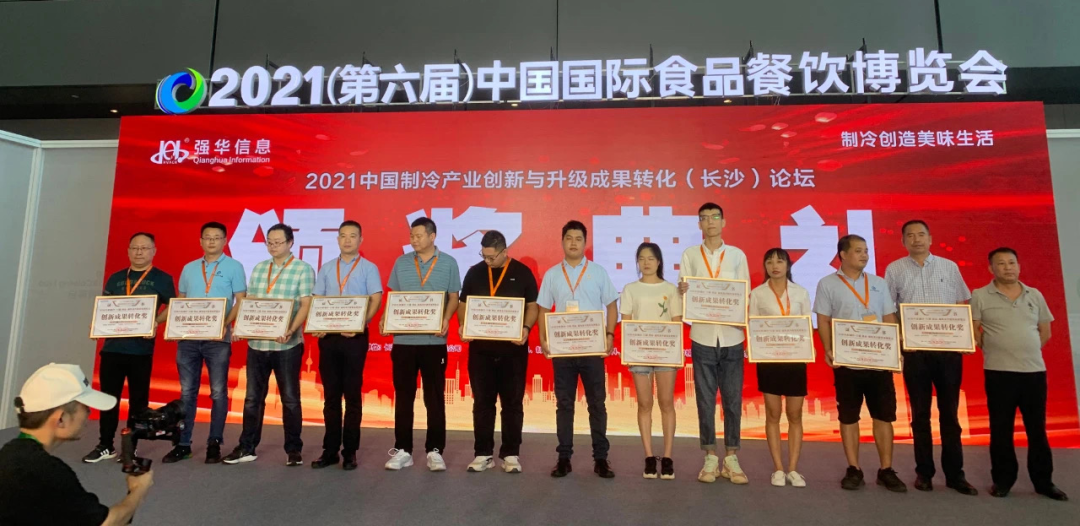 Brand-driven innovation leads
Brand-driven innovation leads
In the future, Fujing will continue to increase investment in research and development, continuously optimize and innovate technology, continuously improve product quality, and provide customers with more complete Welding materials, welding equipment, Welding tools, welding accessories, welding parts processing and other services.
And to provide customers with welding-related consulting and training services, Welding materials selection, research and development and customization, welding equipment, process design, welding program evaluation and optimization, composition and physical performance testing and other one-stop welding services.
Related News