Product
Product Center
About Us
ABOUT US

Was Founded In

HANGZHOU FIRMKIM WELDING TECHNOLOGY CO.,LTD.
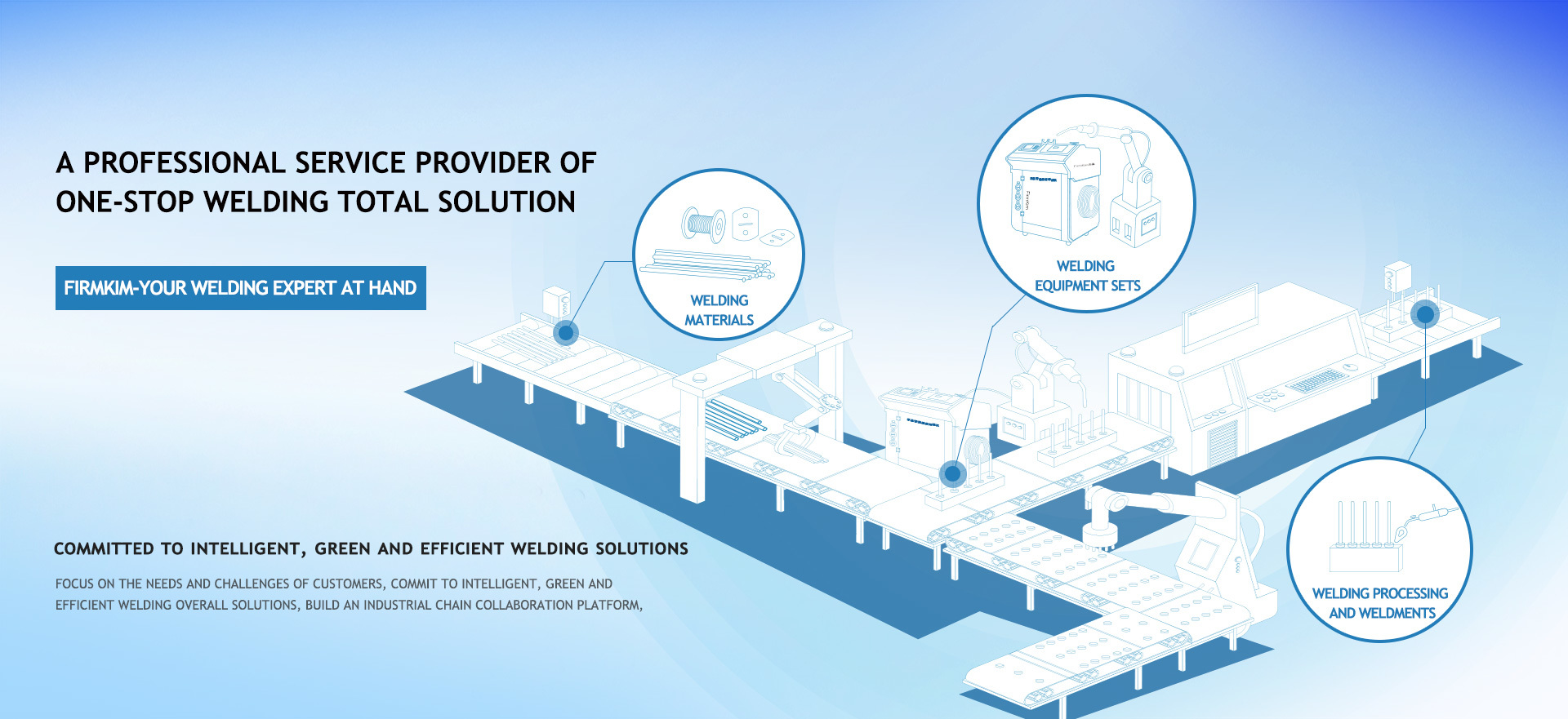
HANGZHOU FIRMKIM WELDING TECHNOLOGY CO.,LTD. was established in 2007 and is a wholly-owned subsidiary of hangzhou huaguang welding new materials co., ltd. (stock code: 688379), a company listed on the science and technology innovation board. The company is committed to intelligent, green and efficient welding solutions, and has joined hands with domestic and foreign experts to focus on welding problems such as non-ferrous metals and heterogeneous metals for a long time.
The company has formed its own unique core technology in the fields of laser welding, induction welding and vacuum welding. By providing different customers with cost-effective customized products and technical services, it helps customers reduce costs and improve competitiveness. The products have been widely used in refrigeration, hvac, electric power appliances, new energy vehicles, nuclear power, semiconductor equipment, energy storage, home appliances and other industries.
News
News Center
Contact us
Contact us
HANGZHOU FIRMKIM WELDING TECHNOLOGY CO.,LTD.
Tel: +86-18594983359
Mail: Firmkim@cn-huaguang.com
Post code: 311112
Add: No. 82, Qihang Road, Renhe Street, Yuhang District, Hangzhou City, Zhejiang Province
Online Message
Dear customer, if you have any comments or suggestions about our products or services, please let us know in a timely manner and we will reply to you as soon as possible.